In Basic knowledge of skin-2, let’s take a look at the Structure of the Skin Surface
Structure of the Skin Surface
Detergents used for the human body are used for the skin. It is very dangerous to make a cleanser for the human body without understanding the skin, and it is not something to be recklessly attempted. Incorrectly made detergents not only cause degeneration of the skin but also cause skin troubles and accelerated aging.
The skin is surrounded by the surface of the human body and plays a role in protecting the human body from stimuli such as air, temperature, and ultraviolet rays without rest. Skin is formed of fat, moisture, protein and minerals, and these have a close relationship with the physiological phenomenon of skin tissue. skin thickness is the thickest On the other hand, the eyelids are the thinnest and are prone to fine wrinkles.
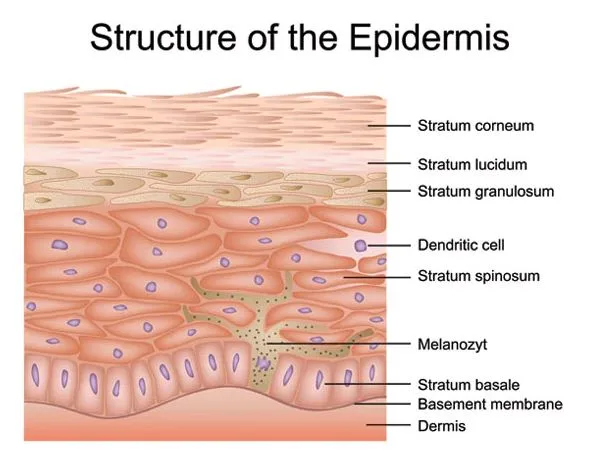
The structure of the skin can be largely divided into three layers from the outer layer: Epidermis, Dermis, and Subcutaneous Tissue. The epidermis is covered with the outermost layer among the three layers and is the thinnest, toughest, and hardest of all cells, and is responsible for moisturizing and protecting the skin. It plays an important function to protect tissues from water loss and damage, and to prevent bacterial invasion. The epidermis is composed of the stratum corneum, the Stratum Lucidum, the Stratum granulosum, the Stratum spinosum, and the stratum basale.
1) stratum corneum
– The stratum corneum is located at the outermost part of the epidermis and is covered with 15 to 30 layers of dead cells with no life, which is tightly adhered to each other and tightly packed with lipid components.
– The outermost layer of the stratum corneum is called the scale layer, and the scale layer does not rest from the epidermis, and unnecessary substances and bacteria are released together and naturally fall off the skin. This peeling off is called epidermal exfoliation.
– The stratum corneum has a water content, and when the water content decreases, the stratum corneum becomes thicker, the skin texture becomes rough, and the skin aging is accelerated, so the proper water content must be maintained.
2) Stratum Lucidum
– Consists of 2-3 layers of lifeless, non-nucleated, small, transparent cells.
– It plays a role in blocking light and is located just below the stratum corneum, and a protein called Elaidin prevents moisture from penetrating and makes the skin shiny.
3) Stratum granulosum
– The Stratum granulosum is formed of granular cells and is a group of equilibrium, spindle-shaped cells composed of 2 to 5 layers of cells.
– The Stratum granulosum is a layer that contains numerous keratohyalins in the protoplasm and is the layer where keratinization begins.
– When keratohyalin, a keratin enzyme, is produced in large quantities, deterioration of the skin begins and the cells become dry.
– The main components of keratohyalin are lipids, proteins and sugars.
4) Stratum spinosum
– It is the thickest layer of the epidermis and consists of 5 to 10 layers.
– There are spine-like protrusions on the surface of cells, which are connected to neighbouring cells in the form of spines, so it is called the ‘prickle layer’ or ‘Stratum spinosumr’ in the sense of a layer with poles.
– There are Lankerhans cells in charge of immunity in the Stratum spinosum, and there is lymph fluid between the multi cells of the Stratum spinosum, which helps supply nutrients and blood circulation to the skin.
5) stratum basale
– It is located in the deepest part of the epidermis and is located at the border with the dermis.
– In the stratum basale, cell division occurs, and pigment cells are distributed among the basal cells to create skin colour and protect the skin from ultraviolet rays.
– The moisture content of the stratum basale is 60~70%, and the pH is about 7.2.
– Cells initially formed in the stratum basale are pushed up to reach the Stratum spinosum and the Stratum granulosum, and when they reach the top of the Stratum granulosum, the cells are not supplied with nutrients and the epidermal cells naturally die. It takes about 14 days.
– Dead cells are pushed up further due to cell division of the stratum basale to form the vinyl layer of the stratum corneum, and in the stratum corneum, dead cells are released along with unnecessary substances and bacteria after about 14 days and naturally fall off the skin.
As we have seen above, the skin of the human body is constantly making new cells while we are resting. As the generated cells are pushed up to the outside of the skin, the vitality of the skin is lost due to the influence of dead cells, and they are accumulated on the outer surface of the skin and are separated from the skin. This process takes about 28 days. The stratum corneum protects the skin, protects the tissue from moisture loss, and also serves to prevent the invasion of bacteria, but excessive accumulation causes problems in the process of making new skin cells, causing skin trouble.
-The Nature Atelier-
If my article was helpful, please comment and visit my SNS. It will be a great help for me to continue running the site.
Twitter
https://twitter.com/Atelier_Eden
Instagram
https://www.instagram.com/the.natureatelier